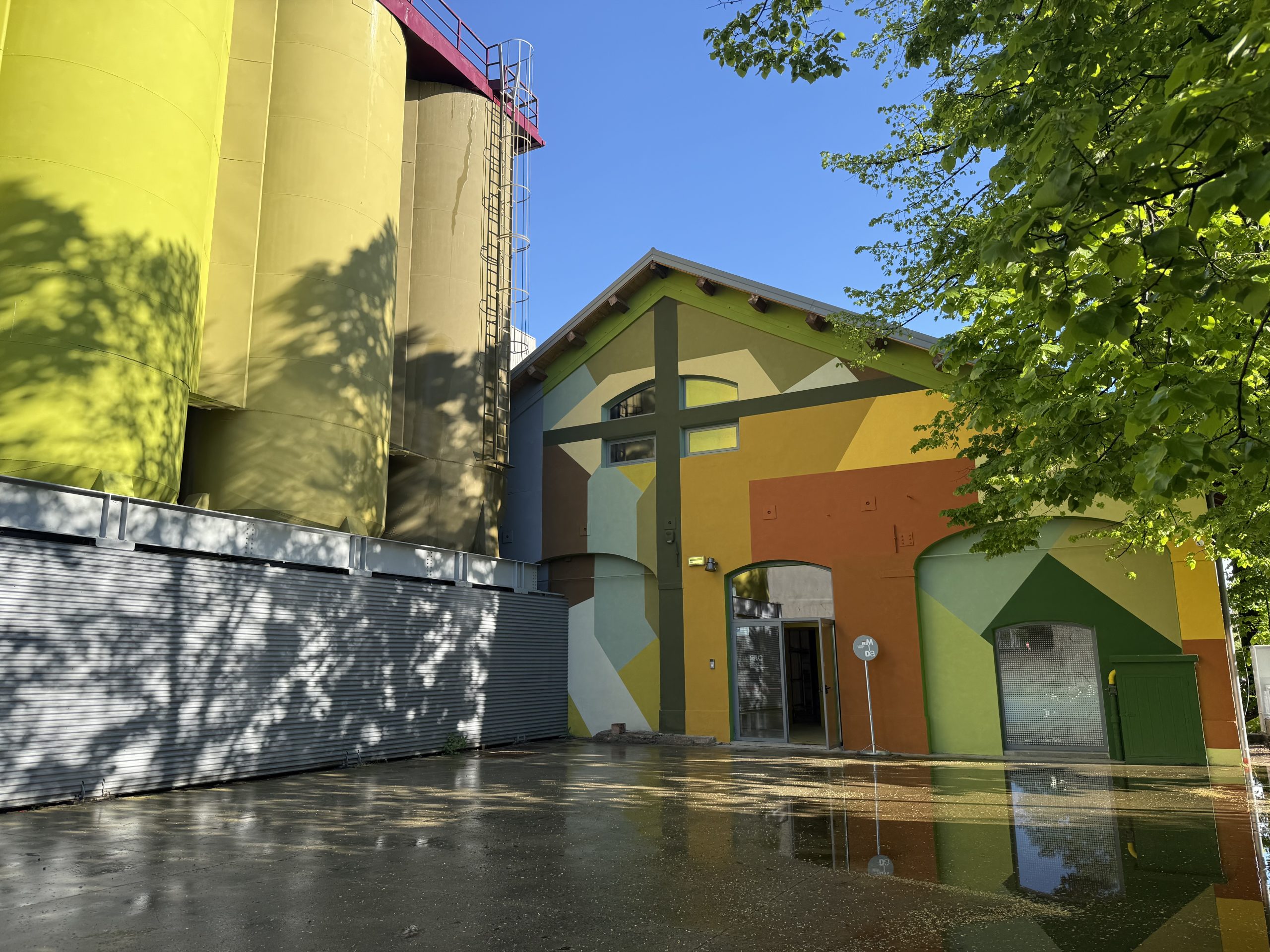

Constructing Modern Knowledge is the series of conference / workshops on education and technology lead by Gary Stager and Sylvia Martinez since 2008.
It has mostly been hosted in the states, and I attended the summer 2024 event in Manchester, New Hampshire and enjoyed making musical instruments with colleagues using servo motors, programming the BBC micro:bit with MicroBlocks.
We were told it might be the last in the series but were surprised to learn that Gary & Sylvia had planned to run an event at the Reggio Emilia Foundation in Reggio Emilia, Italy in April 2025 – so when it was confirmed, I jumped at the chance to go!
Unlike my summer experience, this event focussed on both the Reggio Emilia approach to early childhood education and the place of computation in progressive pedagogy and education, and asked the question “what role for computation?”.
And it was enlightening, uplifting and rewarding.
The Reggio Emilia approach
Although I knew of the Reggio Emilia approach, I hadn’t understood its history, its local context nor the detail of its focus on aesthetics (as opposed to anaesthetics!) in education.
The history since the close of the second world war demonstrates what can happen when a town sees children as an asset and takes care to respect their rights.
It was a delight to work in the associated Remida centre, next door to the foundation. Remida undertakes creative recycling, recovering from a network of 100 local companies about 15 tons per year of material destined for disposal, which is put back into circulation through projects and a distribution service to about 300 institutions which are associated with the Reggio Emilia approach. We were treated to talks about the approach used in schools and in particular the ‘atelier’ – a room in each school run by an additional education professional, the ‘atelierista’ often an artist or designer by training. The focus was on experiencing ‘materiality’ and the recycling centre was perfect as a venue to see first hand the way surplus materials were organised and re-distibuted to enhance children’s ‘research’ in building their knowledge.

I thoroughly enjoyed returning to childhood to explore these ideas in three workshops.
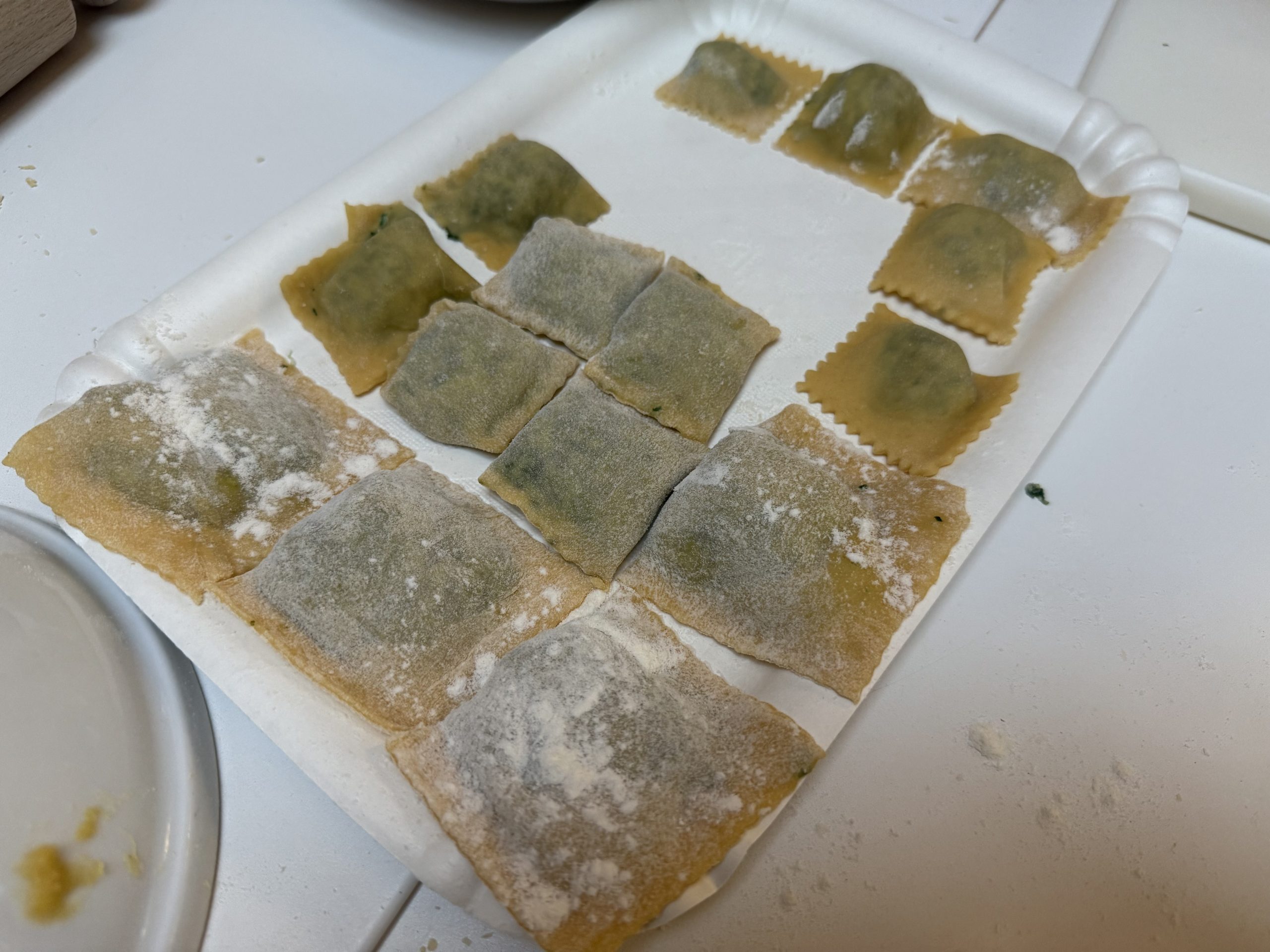
Firstly we all worked together to make pasta, and eat it…

…secondly in a group of five, we explored ‘fast’ and ‘slow’ in light…

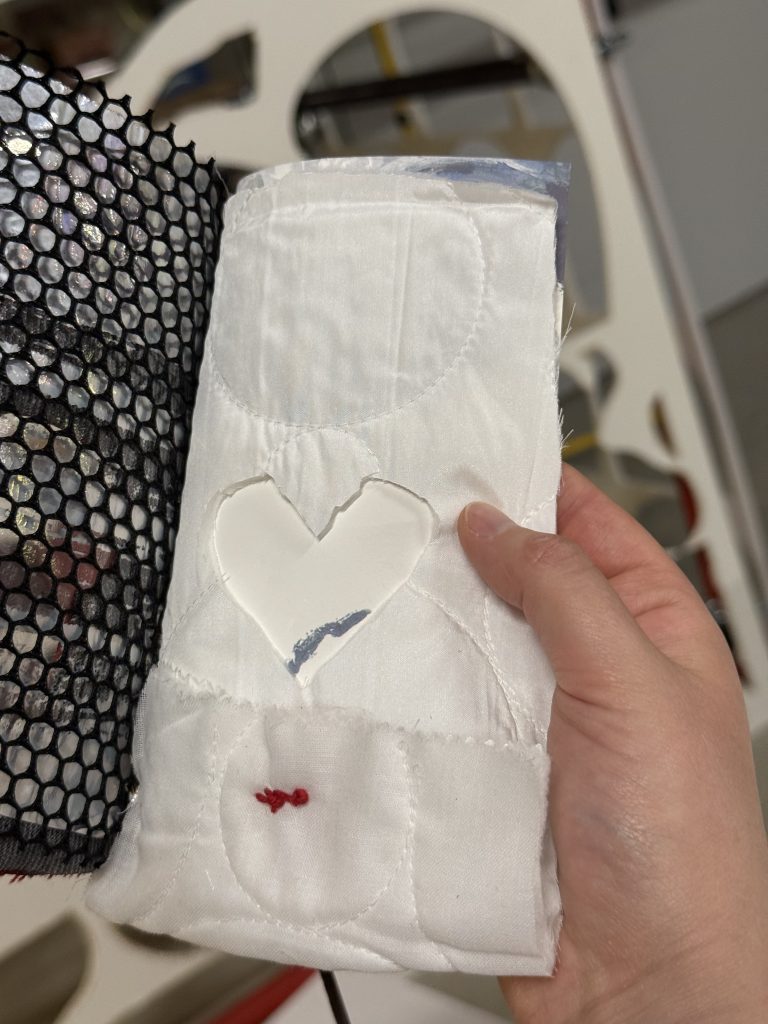
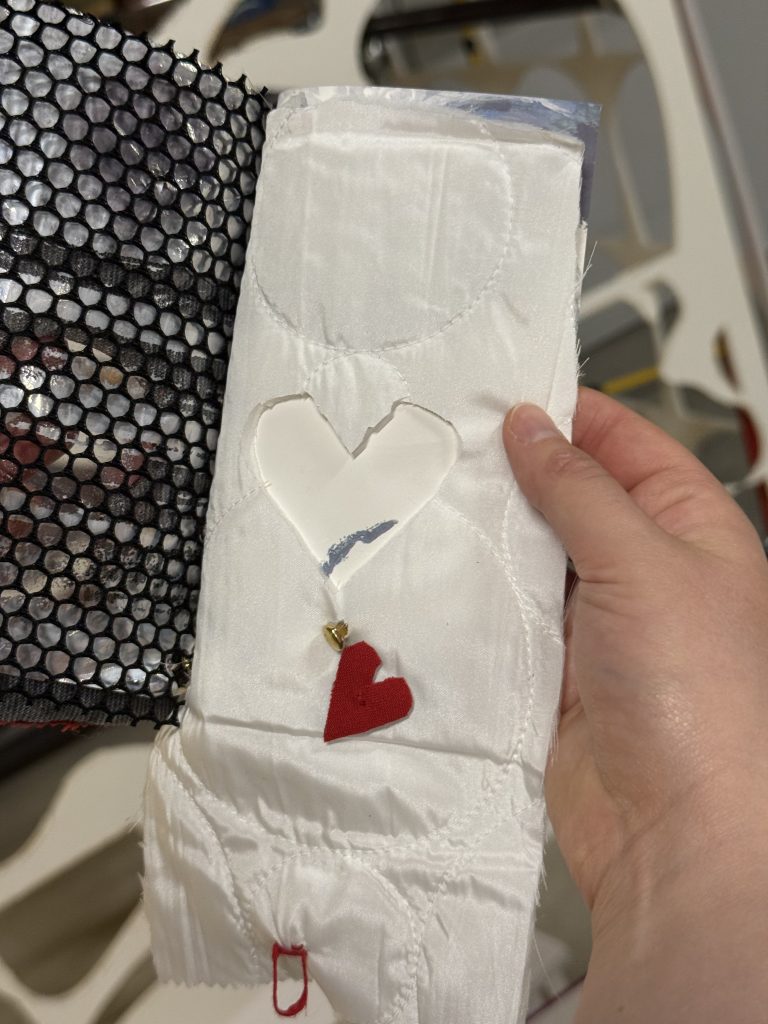
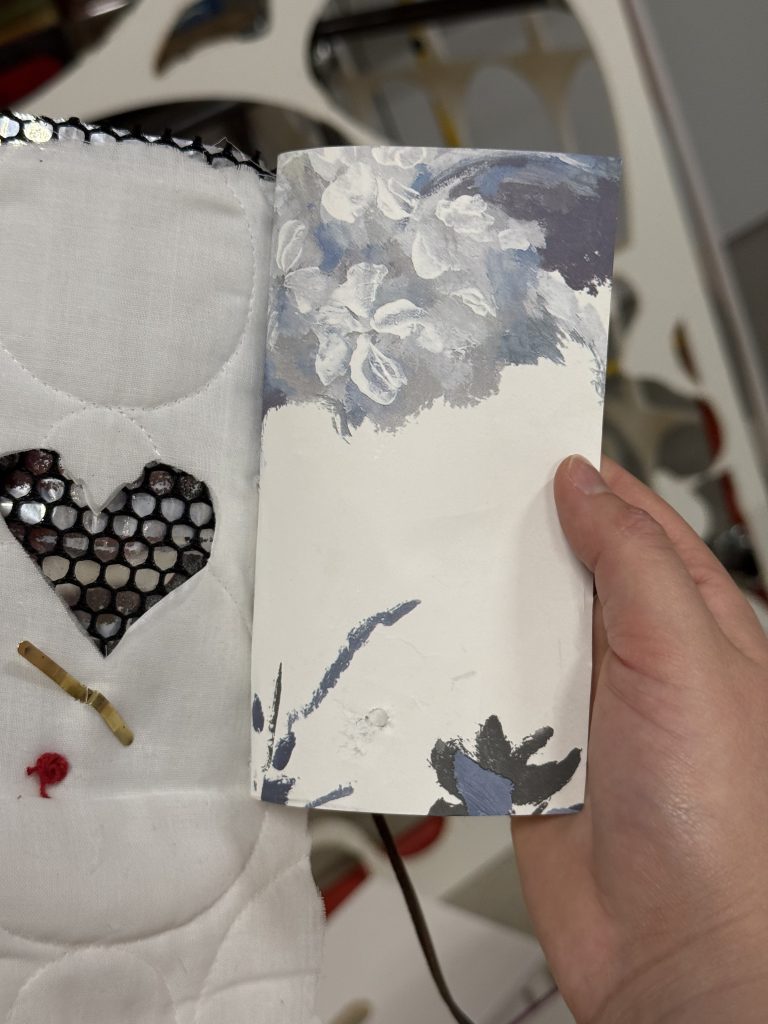
…and thirdly, also in a group of five we created a book, bound in brass and leather from five sheets of material chosen one each by the participants, but no words…
The place of computation
The combination of values regarding early childhood education, re-cycling and re-use, and civic backing for the local education system was intoxicating, but behind all the excitement there was a burning question about the place of computing and computational thinking.
Gary gave us his take on the relationship, with a solid constructionist analysis based on his lifelong love affair with Seymour Papert and his work – just lovely.

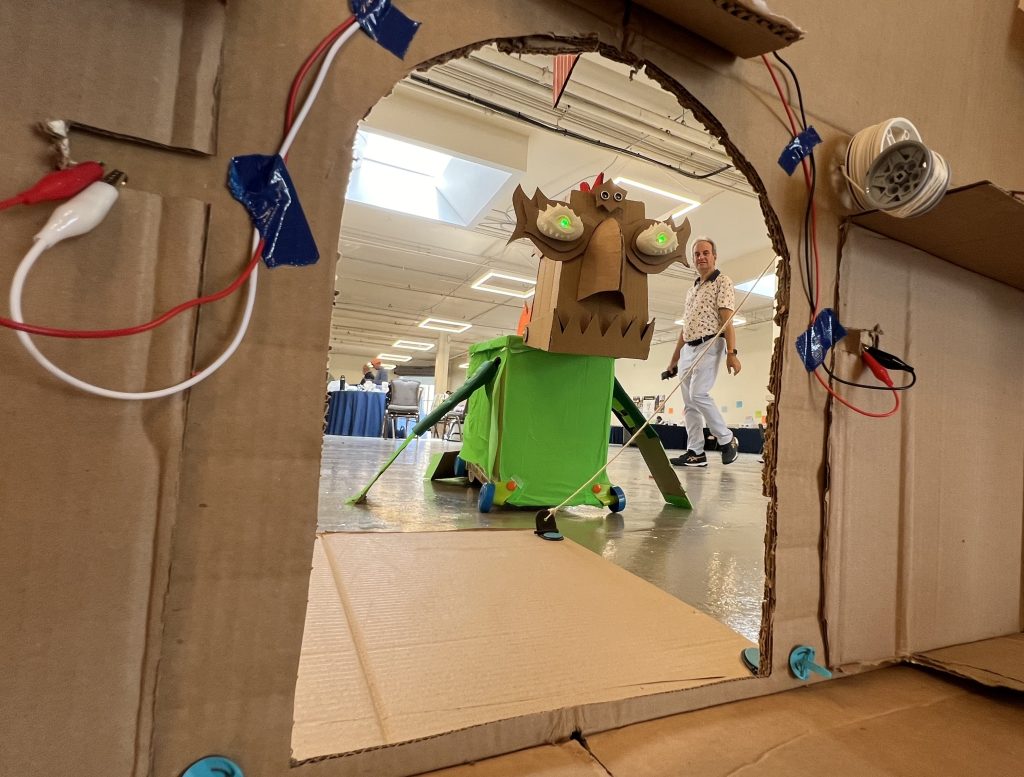
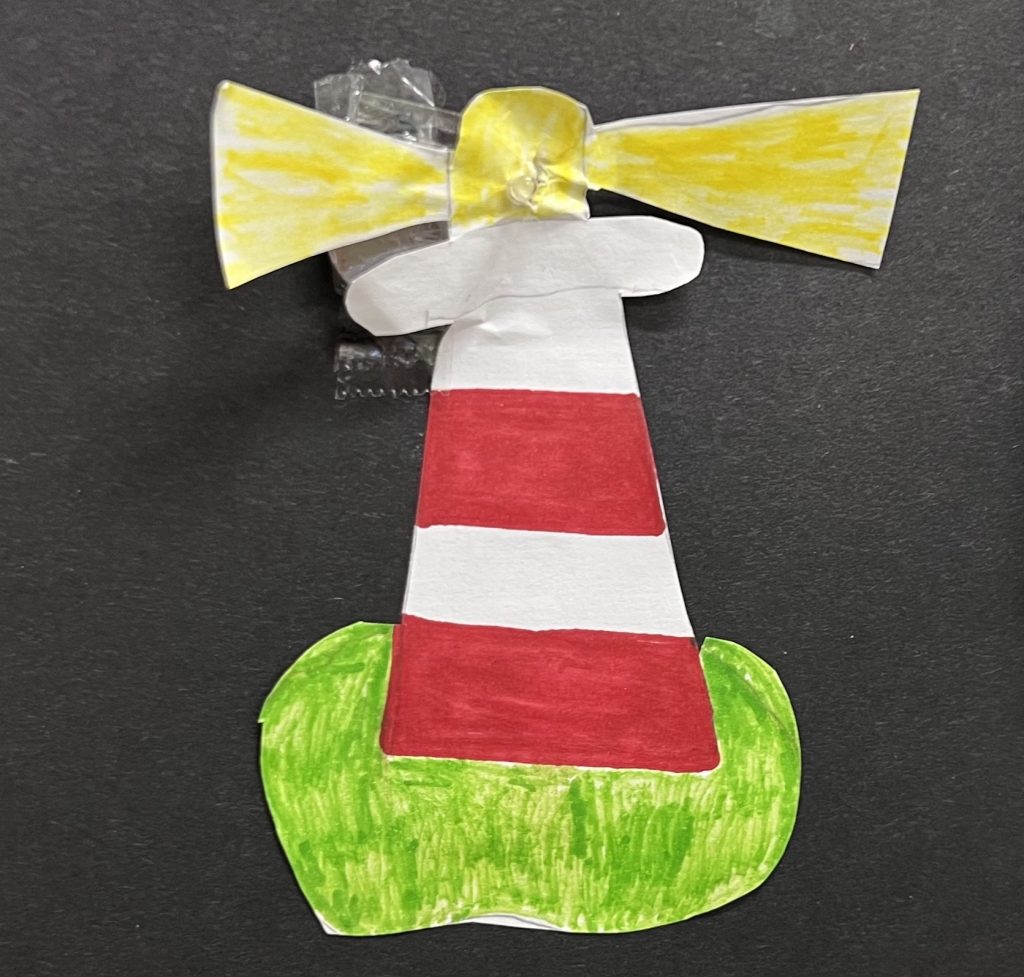
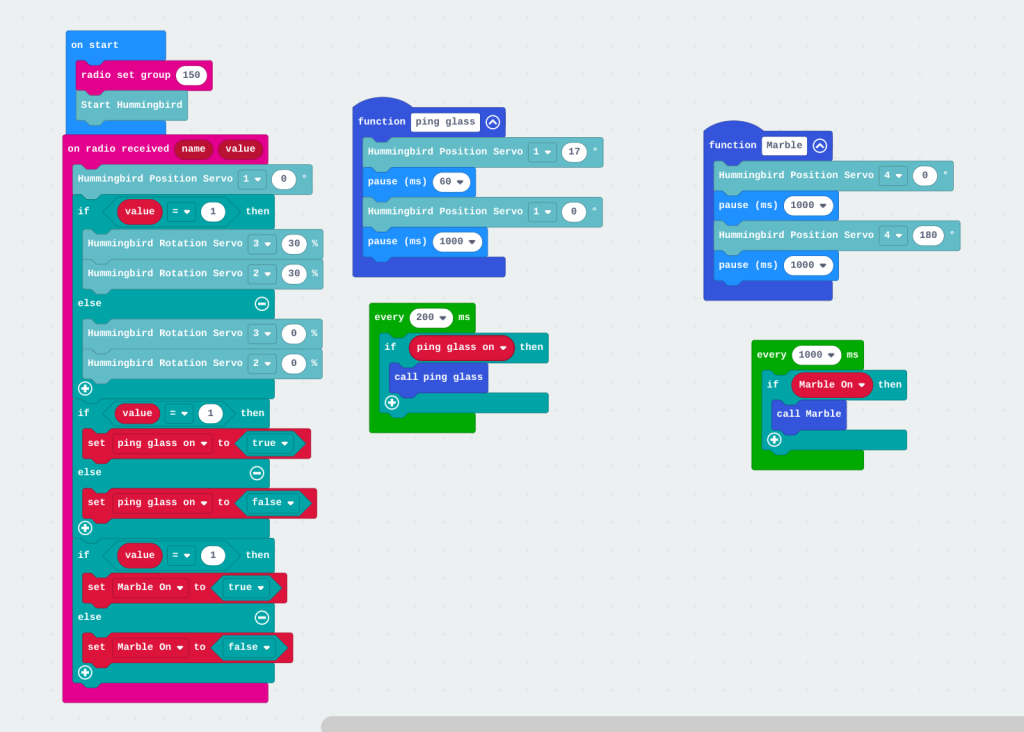
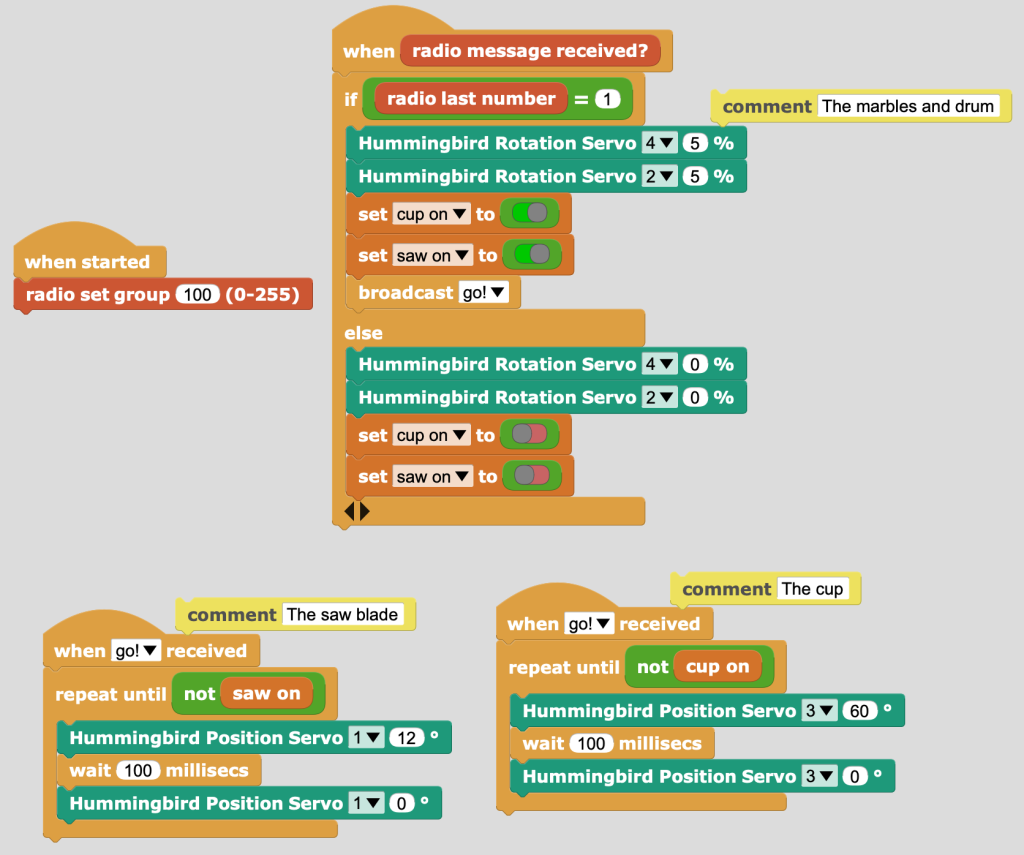
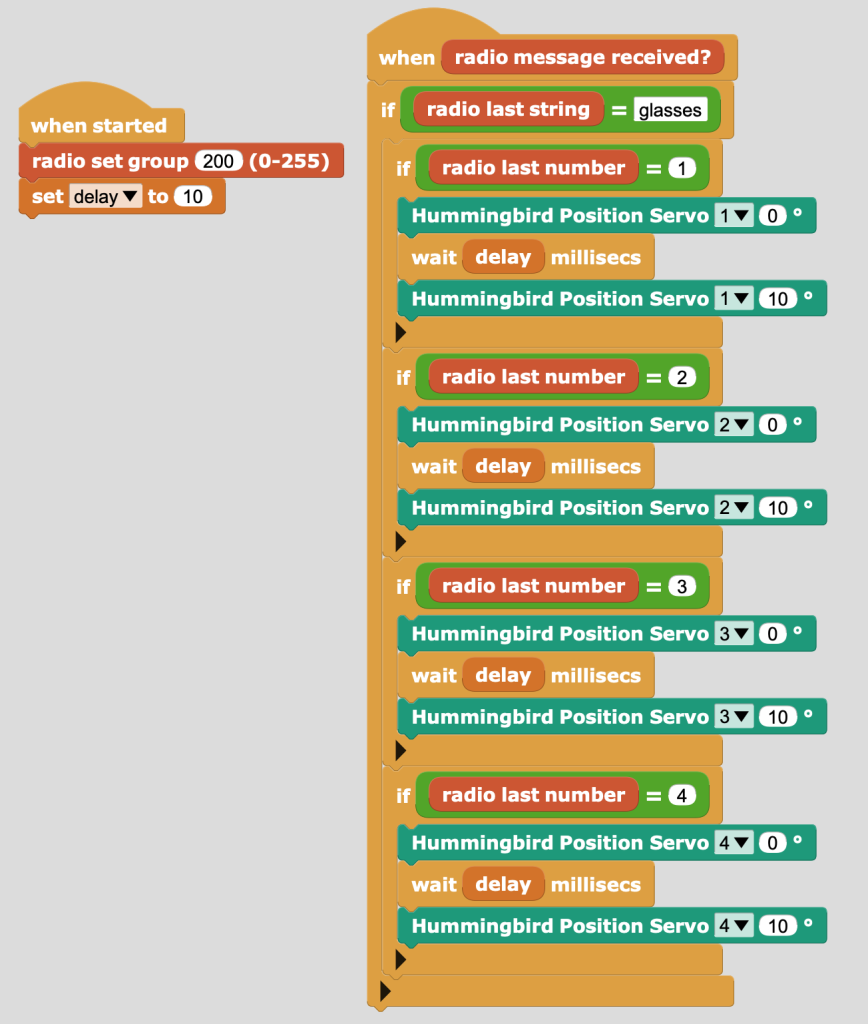
Gary also invited us to invent a simple Easter egg dispensing device using Micro:bit and the Hummingbird equipment – the Easter Bunny is sick, help!.
Against challenging time pressure, the group of three I was in enjoyed making this, both an ambulance for the sick bunny and a cart with eggs that would drop if it encountered an obstacle:
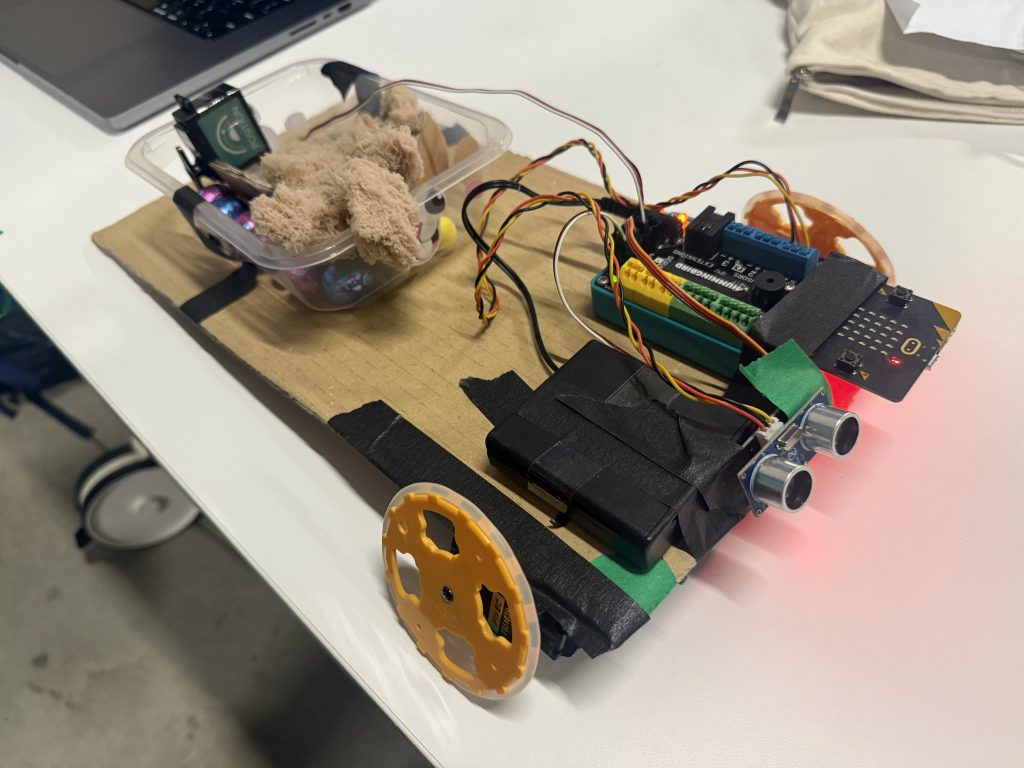
Conclusion
My personal takeaway was in relation to the 100 languages concept of the Reggio Emilia approach as eloquently introduced in this poem by founder Loris Malaguzzi:
No way. The hundred is there.
The child
is made of one hundred.
The child has
a hundred languages
a hundred hands
a hundred thoughts
a hundred ways of thinking
of playing, of speaking.
A hundred always a hundred
ways of listening
of marvelling of loving
a hundred joys
for singing and understanding
a hundred worlds
to discover
a hundred worlds
to invent
a hundred worlds
to dream.
The child has
a hundred languages
(and a hundred hundred hundred more)
but they steal ninety-nine.
The school and the culture
separate the head from the body.
They tell the child:
to think without hands
to do without head
to listen and not to speak
to understand without joy
to love and to marvel
only at Easter and Christmas.
They tell the child:
to discover the world already there
and of the hundred
they steal ninety-nine.
They tell the child:
that work and play
reality and fantasy
science and imagination
sky and earth
reason and dream
are things
that do not belong together.
And thus they tell the child
that the hundred is not there.
The child says:
No way. The hundred is there.Loris Malaguzzi, 1996, translated by Lella Gandini
I have emboldened the lines in the middle that sing to me and that echo so much of my own work in the design of education throughout my working life.
But I couldn’t help feeling that in the computational media, genre and tools, there were so many additional ‘languages’ .
I would include programming, spreadsheets, databases, word processors, drawing packages, presentation tools, digital audio & video, hypertexts, and so much more. In each case they are tools for expressing ideas, but have the additional value of bringing support for evaluation of those ideas as the child sees what does and doesn’t work on the computer.
This feedback loop of ‘expression’ and ‘evaluation’ is what I call ‘expressive constructivism‘ in my Phd.
Furthermore, I explained how technology supports learning in both expression and evaluation.
But for me, even more potently now making the case for computation, is that we can use computation to develop our own tools – a meta-level of expression and evaluation that may make a million languages in my humble view!
Many thanks to Gary and Sylvia and the Reggio Emilia ateliers for their wonderful programme of activities and inputs, but most importantly to all the experienced, thoughtful and open educators who participated with me and made the time so fruitful with their enthusiastic efforts and deep dialogue.

























![@AttyMassNS "At the recent [CESI] Conference, we mentioned our plans to explore decomposition and patterns/generalisations through Damhsa/Irish dancing. Integrates with/comhthathú le Seachtain na Gaeilge" March 2018](http://blog.richardmillwood.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/AttyMass-NS-tweet-about-Computational-Thinking-and-Irish-Dancing.jpg)


